VFDs and inverters are electronic devices often used to convert the power of various electrical applications in industry and households. While both work with electricity and are frequently considered similar, their functions and intended uses differ. Understanding the fundamental differences between the two is essential in choosing the correct device for your needs.
This article discusses the VFD vs Inverter comparison, definitions, key differences, and related information before you choose the best device.
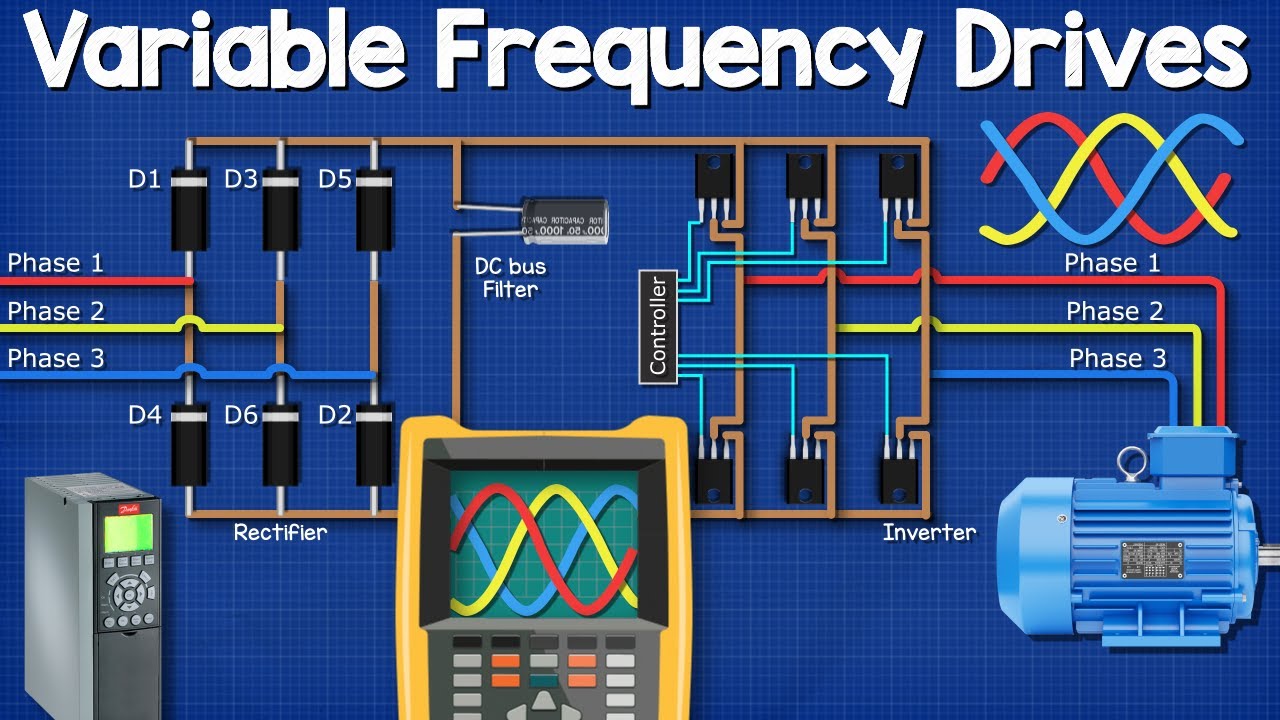
VFD vs Inverter: Definition
What is a VFD?
A VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) is an electronic device that controls the speed and torque of an AC electric motor by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. A VFD works by converting AC power from a power source into DC through a rectification process. Internal inverter technology converts This DC back to AC with adjustable frequency and voltage. The VFD enables precise motor speed control by adjusting the frequency and voltage.

VFDs are widely used in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, Conveyor belts in the manufacturing industry, water pumps to reduce power consumption, and industrial fans due to their high efficiency as they can adjust motor speed as needed and reduce electric current spikes during motor startup.
What is an Inverter?
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Inverters usually provide AC power to devices that can only work with alternating current.
An inverter converts DC electricity into AC with a fixed frequency (usually 50 Hz or 60 Hz) that suits the device’s needs. A DC power source, such as a battery or solar panel, enters the inverter through an inverter cable.

Generally, inverters are applied to solar energy systems to convert solar panel power into AC electricity, backup power systems (UPS) for electronic devices, and power conversion for household devices in vehicles or locations without a power grid.
See the inverter application for detailed information.
VFD vs Inverter: Key Differences
While a VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) and an inverter serve the same function in an electrical system, they fundamentally differ in function, application, and characteristics. Here is an explanation of the main differences:
Main Function
VFDs are designed to control the speed and torque of AC electric motors by regulating the frequency and voltage applied to the motor. This function makes VFDs suitable for applications that require precise motor speed control, such as conveyor belts, pumps, or HVAC systems.
On the other hand, inverters have the primary function of converting direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Inverters often power household electrical devices from DC sources, such as batteries or solar panels.
Output Control
There is also a notable difference between the two. VFDs can dynamically change the output frequency and voltage according to the needs of the electric motor, enabling speed and torque control. Conversely, inverters can generate alternating current (AC) with a fixed frequency and voltage (usually 50 Hz or 60 Hz) to operate electrical devices.
Main Application
VFDs are used in the industrial sector to control electric motors in conveyor belt applications, water pumps, and production machinery. They are also commonly used to adjust the speed of fans and compressors based on building temperature requirements.
Inverter applications based on renewable energy, such as solar panels, turbines, and batteries, are widely used in the household sector.
Technology
VFDs have more complex technology than inverters, which involve precise frequency and voltage regulation. VFDs are also often equipped with features such as soft start, regenerative braking, and torque control.
Energy Efficiency
Both have their designation and efficiency. VFDs are very efficient for motor control as they can reduce power consumption by regulating the motor speed as needed. This helps save energy, especially in systems that require speed variation.
While inverters, as per their primary function, are very efficient in converting DC power into AC, they are not designed to regulate the energy consumption of devices that use AC electricity.
Cost
In comparison, VFDs are more expensive than inverters based on technological complexity and other aspects, such as specific applications and installation processes requiring specialized skills. Inverters are more affordable and easy to install, especially for household or off-grid applications.
Summary
| Aspect | VFD | Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Controls motor speed/torque. | Converts DC to AC. |
| Output Control | Adjustable frequency and voltage. | Fixed frequency and voltage. |
| Applications | Industrial: motors, pumps, fans. | Residential: solar power, UPS. |
| Complexity | More complex technology. | Simpler technology. |
| Energy Efficiency | Optimized for motor control. | Optimized for power conversion. |
| Cost | More expensive. | More affordable. |
VFD vs Inverter: Pros & Cons
Here is the list of pros and cons between VFD vs. Inverter.
VFD Pros:
Reduces power consumption by adjusting motor speed to match demand, which enables high energy efficiency.
It allows for accurate speed and torque control, which is ideal for industrial applications.
Reduces mechanical stress on motors during startup, prolonging motor life.
Advanced features like regenerative braking, overload protection, and automated control.
Operates motors more quietly by running them at optimal speeds.
VFD Cons:
More expensive than more straightforward motor control methods.
The complex installation requires expertise for setup and calibration.
It contains sensitive electronic components that may require regular maintenance.
It has limited applications because it’s designed specifically for AC motor control, not general-purpose power conversion.
Inverter Pros:
It has a versatile power conversion
It is generally more affordable than VFDs, especially for household or small-scale use.
Simple installation and operation without complex configurations.
Compatible with renewable energy
Inverter Cons:
It cannot control motor speed or torque; it only provides power conversion.
The output quality depends on its type. Modified sine wave inverters, for example, may not be suitable for sensitive electronics.
Dependence on DC source: Inverters require a consistent DC input, such as from a battery or solar panel.
VFD vs Inverter: Which One is The Best for Your Application?
Choosing between a VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) and an inverter depends entirely on your application and specific needs. Both devices are used in electrical systems but serve different purposes, making them suitable for various scenarios.
VFDs could be the best answer if you need precise motor speed and torque control for industrial processes where equipment must adapt to varying workloads.
Inverters could be the best choice if you need a device to convert DC into AC power for applications such as solar power systems, off-grid, backup power for sensitive electronics, and portable generators. See inverter vs. generator for detailed information.
Final Thoughts
Although considered to have the same energy conversion function, many VFD vs. Inverter comparisons exist due to application specificity and technology.
Plan your device with Joeyoung inverter manufacturer, which can provide a wide range of OEM/ODM customization services to meet your unique project requirements.
Frequently asked questions
No, an inverter cannot function as a VFD because it cannot adjust frequency and voltage dynamically to control motor speed.
VFDs are typically compatible with three-phase AC motors. Compatibility with single-phase motors or special motor types requires specific configurations.
VFDs can be used in residential applications, such as controlling speed in HVAC systems or water pumps, but they are more common in industrial setups.
Choose a VFD for precise motor speed and torque control in industrial applications. Choose an inverter for converting DC power to AC, such as solar or backup systems.

In its use over time, inverters may fail due to wear and tear, age, or improper usage. Understanding inverter replacement is an essential investment of knowledge to maintain your electrical system’s performance, safety, and efficiency.

This article contains things you should know about two main types of frequencies to be compared: low- requency vs high frequency inverters.

As the oldest country implemented solar panel system, USA has the number of manufacturer that produce inverters.
The article below contains the top 10 inverter manufacturers 2024 in the USA.
Authors
-
Passionate to education and renewables energy make me enthusiast about making complex technologies accessible to everyone by translating it into a practical and easy to understand. Let's learn and grow together!
View all posts
-
hi I am Jim, an inverter specialist with over 10 years of experience. I previously worked as an R&D engineer at a leading energy company, focusing on inverter design, optimization, and system integration. I have been involved in the development of key technologies and gained comprehensive expertise in both technical innovation and practical applications. Currently, I focus on professional writing to provide clear analysis and practical insights into inverter technology, contributing to its advancement and broader adoption in the industry.
View all posts


